维吾尔医学与四大物质学
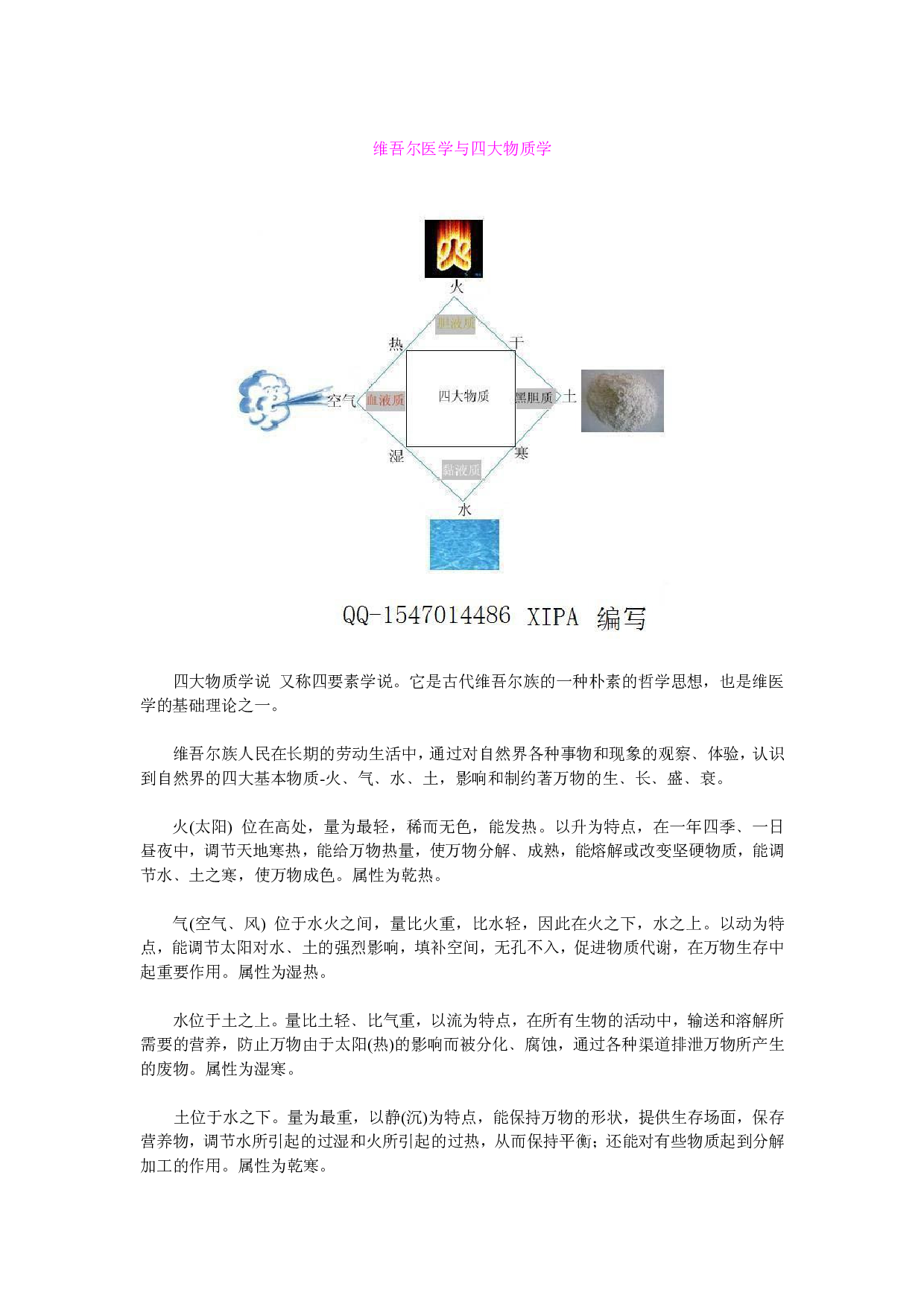
四大物质学说 又称四要素学说 。它是古代维吾尔族的一种朴素的哲学思想 ,也是维医
学的基础理论之一 。
维吾尔族人民在长期的劳动生活中 ,通过对自然界各种事物和现象的观察 ﹑体验,认识
到自然界的四大基本物质 -火﹑气﹑水﹑土,影响和制约著万物的生 ﹑长﹑盛﹑衰。
火(太阳 ) 位在高处 ,量为最轻 ,稀而无色,能发热。以升为特点 ,在一年四季﹑一日
昼夜中 ,调节天地寒热 ,能给万物热量,使万物分解﹑成熟,能熔解或改变坚硬物质 ,能调
节水 ﹑土之寒 ,使万物成色 。属性为乾热。
气(空气 ﹑风) 位于水火之间 ,量比火重,比水轻,因此在火之下 ,水之上。以动为特
点,能调节太阳对水 ﹑土的强烈影响,填补空间,无孔不入,促进物质代谢 ,在万物生存中
起重要作用 。属性为湿热 。
水位于土之上 。量比土轻﹑比气重,以流为特点 ,在所有生物的活动中 ,输送和溶解所
需要的营养 ,防止万物由于太阳 (热 )的影响而被分化 ﹑腐蚀,通过各种渠道排泄万物所产生
的废物 。属性为湿寒 。
土位于水之下 。量为最重,以静(沉 )为特点 ,能保持万物的形状 ,提供生存场面,保存
营养物 ,调节水所引起的过湿和火所引起的过热 ,从而保持平衡;还能对有些物质起到分解
加工的作用 。属性为乾寒 。
Uighur medicine
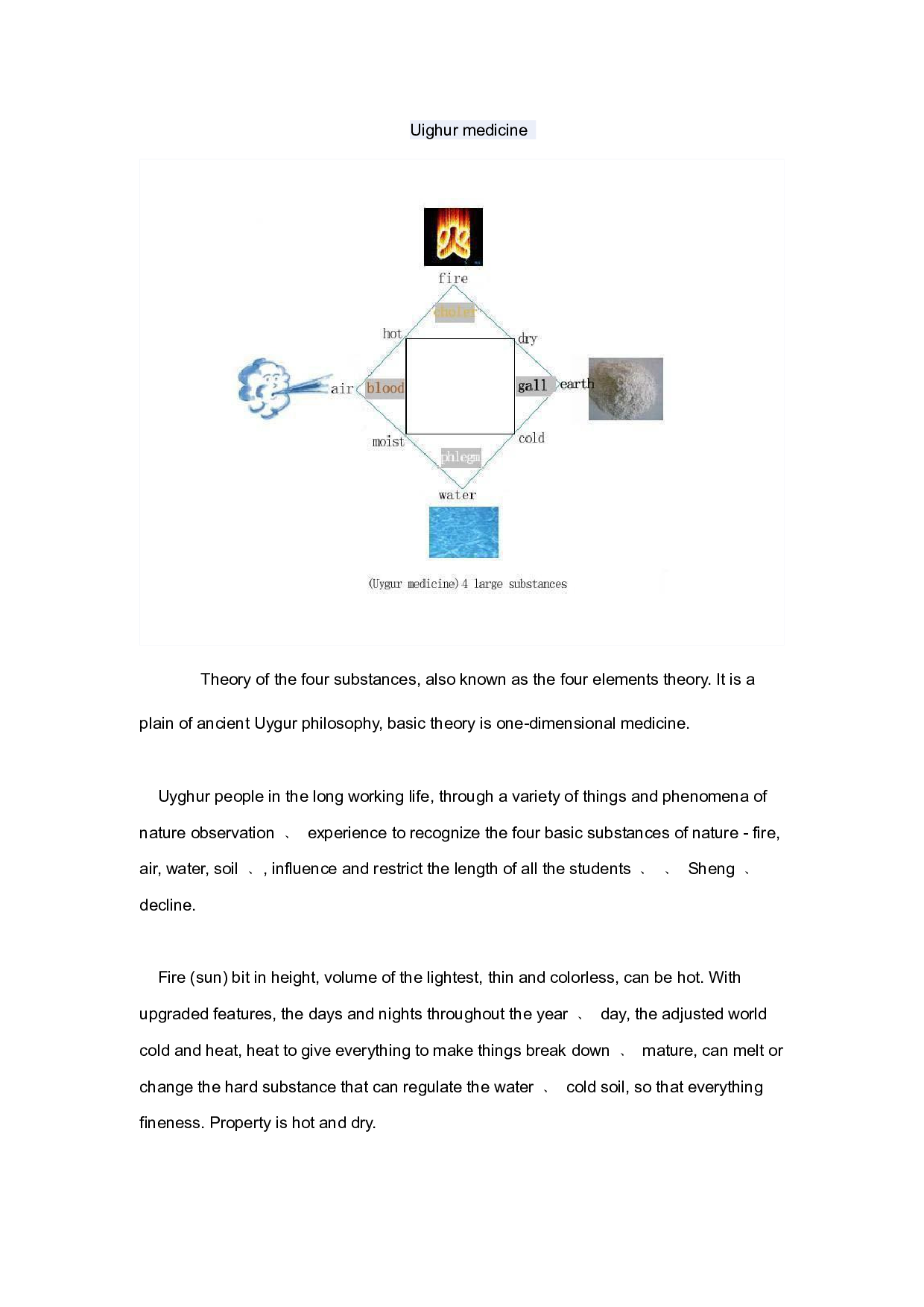
ﺱﺎﺋ ﻯ Theory of the four substances, also known as the f our elements theory. It is a
plain of ancient Uygur philosophy, basic theory is one-dimensional medicine.
Uyghur people in the long working life, through a variety of things and phenomena of
nature observation ﹑ experience to recognize the four basic substances of nature - fire,
air, water, soil ﹑, influence and restrict the length of all the stud ents ﹑ ﹑ Sheng ﹑
decline.
Fire (sun) bit in height, volume of the lightes t, thin and colorless, can be hot. With
upgraded features, the days and nights throughout t he year ﹑ day, the adjusted world
cold and heat, heat to give everything to make thin gs break down ﹑ mature, can melt or
change the hard substance that can regulate the wat er ﹑ cold soil, so that everything
fineness. Pr
维医基础理论(汉英维).pdf